Intelligent Part Numbering Scheme For Relays
This article outlines how to create an intelligent part numbering scheme for Relays, and how you can accurately manage this at scale
A relay is an electrical switch that controls the flow of current in a circuit. It is commonly used to control high-power devices with low-power signals. A relay consists of a coil, which when energized, creates a magnetic field that pulls a set of contacts together, allowing current to flow through the circuit. The main purpose of a relay is to provide a safe and reliable means of controlling electrical circuits.
To create a part numbering scheme for relays, there are several characteristics you might take into consideration. Here are 6 as an example:
1. Relay type: This characteristic could identify the type of relay, such as “electromechanical,” “solid-state,” or “reed.”
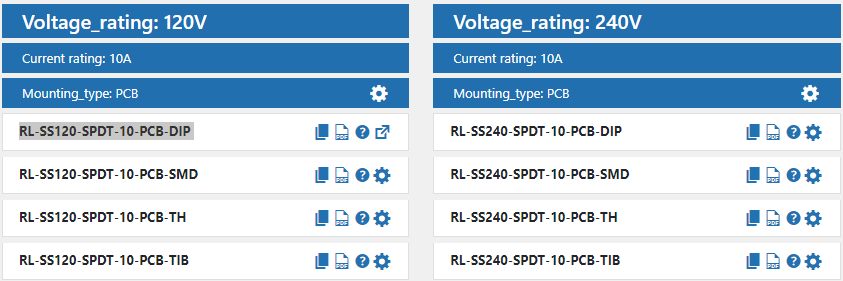
2. Voltage rating: This characteristic could specify the voltage range or rating of the relay, such as “12V,” “24V,” or “120V.”
3. Contact configuration: This characteristic could specify the contact arrangement of the relay, such as “SPDT,” “DPDT,” or “4PDT.”
4. Current rating: This characteristic could specify the maximum current the relay can handle, such as “10A,” “20A,” or “30A.”
5. Mounting type: This characteristic could specify the mounting configuration of the relay, such as “PCB Mount,” “Panel Mount,” or “DIN Rail Mount.”
6. Package type: This characteristic could identify the package type of the relay, such as “DIP,” “SMD,” or “Through-hole.”
To create the actual part number, you could assign a unique code to each option for each characteristic. For example, you could use an abbreviation for the range (e.g. RL for Relays) and then for the product line (e.g. E for Electromechanical), and so on. Then, you can combine the codes for each characteristic to form the complete part number. For example, a relay with the following characteristics:
Solid-state relay with 12V voltage rating, SPDT contact configuration, 20A current rating, DIN rail mount, and through-hole package type.
This might result in a part number that looks like this: RL-SS12-SPDT-20-DIN-TH
Or for some further examples:
Reed relay with 24V voltage rating, DPDT contact configuration, 10A current rating, panel mount, and SMD package type: RL-R24-DPDT-10-PNL-SMD
Electromechanical relay with 120V voltage rating, 4PDT contact configuration, 30A current rating, PCB mount, and through-hole package type: RL-E120-4PDT-30-PCB-TH
You can then use this part number as a unique identifier for the relay in your inventory management system or product catalog.
How can this be done accurately at scale?
PDE is designed to make the definition, management and generation of these part number schemes easy to manage at scale.
Rules for how the product codes should work are entered into the system and then the system can generate the most complicated combinations accurately.
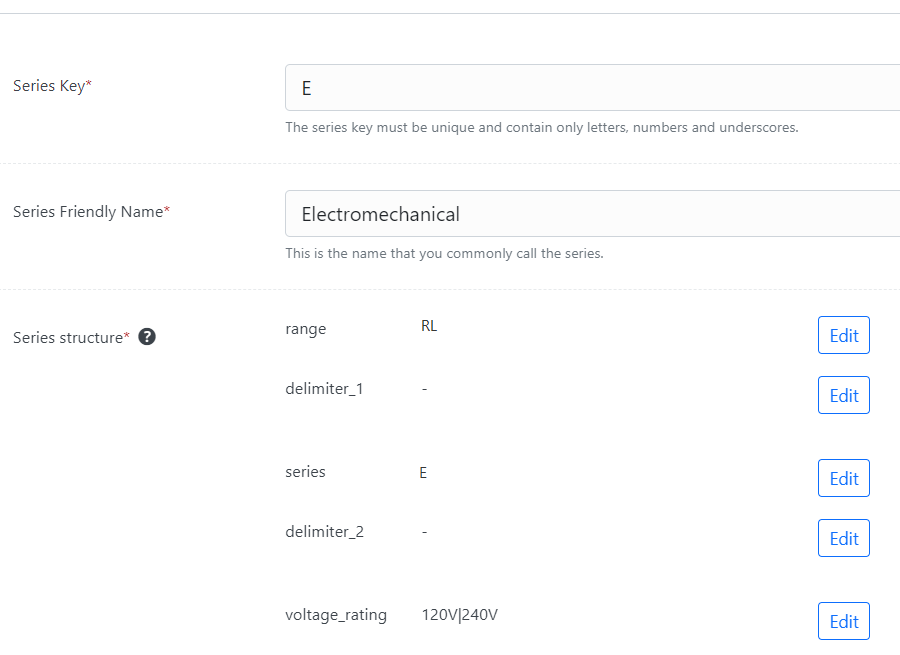
Setting up a the structure of a product series in PDE is straight forward.
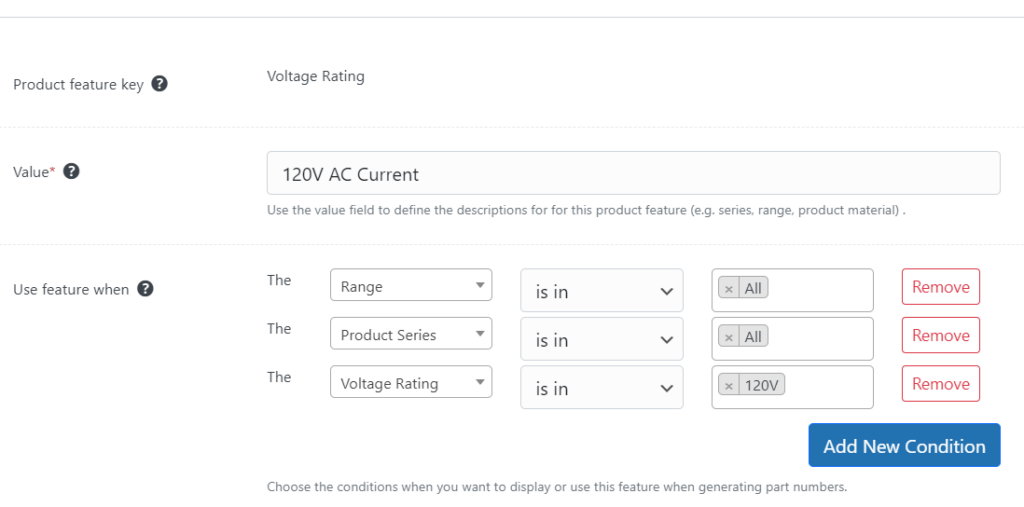
Once you have the structure defined, you can add feature data like voltage rating and control how and where features appear using simple to define rules.
Once you have loaded your data head to the generator.
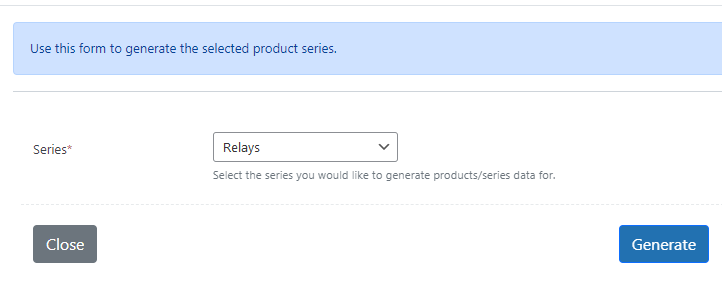
It will take seconds to generate hundreds of accurate web pages, data sheets and series overview.
The best way to see if Product Data Engine is a good fit for your requirements is to take a look at our 3 minute product tour. We would love to show it to you and see if it is a good fit.
