
Intelligent Part Numbering Scheme For Pumps
This article outlines how to create an intelligent part numbering scheme for Pumps, and how you can accurately manage this at scale
A pump is a device that moves fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries, by mechanical action. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps.
To create an intelligent part numbering scheme for Pumps, begin by assigning each of the pump’s six characteristics a letter or number. This will be the foundation of your numbering system. After the characteristics have been assigned, create a numerical structure for the part number. This structure should be designed to make the part number easy to read and remember. For example, each number or letter could be separated by a hyphen or a space to make the number distinct and easy to read. Additionally, assign each assigned letter or number a specific meaning. This will help to ensure that the part number is organised and logical. Finally, create a system for the part numbers to follow. This system should make it easy to add new numbers and to track the modifications of existing parts. By following these steps, you can create an intelligent part numbering scheme for Pumps that is both organised and efficient.
1. Product type – This characteristic could identify the type of pump, such as ‘Centrifugal Pump,’ ‘Submersible Pump,’ etc.
2. Voltage rating – This characteristic could specify the voltage range or rating of the pump, such as ‘120V,’ ‘240V,’ ‘480V,’ etc.
3. Flow rate – This characteristic could specify the flow rate of the pump, such as ’20GPM,’ ’50GPM,’ ‘100GPM,’ etc.
4. Motor type – This characteristic could identify the type of motor used in the pump, such as ‘AC Motor,’ ‘DC Motor,’ etc.
5. Mounting type – This characteristic could specify the mounting configuration of the pump, such as ‘Horizontal,’ ‘Vertical,’ ‘Wall Mount,’ etc.
6. Pressure rating – This characteristic could specify the pressure rating of the pump, such as ‘Low Pressure,’ ‘High Pressure,’ etc.
To create the actual part number, you could assign a unique code to each option for each characteristic. For example, you could use the abbreviation for the range (e.g.PU for Pumps) and then a 3-digit code for the product type / series (e.g. CP for Centrifugal Pump, SP for Submersible Pump, etc.), the first 2-digits of the voltage rating (e.g. “12” for 120V, “24” for 240V, etc.), and so on. Then, you can combine the codes for each characteristic to form the complete part number. For example, a pump with the following characteristics:
- Product type – Centrifugal Pump
- Voltage rating – 120V
- Flow rate 50GPM
- Motor type – DC Motor
- Mounting type – Horizontal
- Pressure rating – Low Pressure
This might result in a part number that looks like this: “PU-CP-12-50-DCM-H-LP”
You can then use this part number as a unique identifier for the pump in your inventory management system or product catalog.
How can this be done accurately at scale?
PDE is designed to make the definition, management and generation of these part number schemes easy to manage at scale.
Rules for how the product codes should work are entered into the system and then the system can generate the most complicated combinations accurately.
Setting up a the structure of a product series in PDE is straight forward.
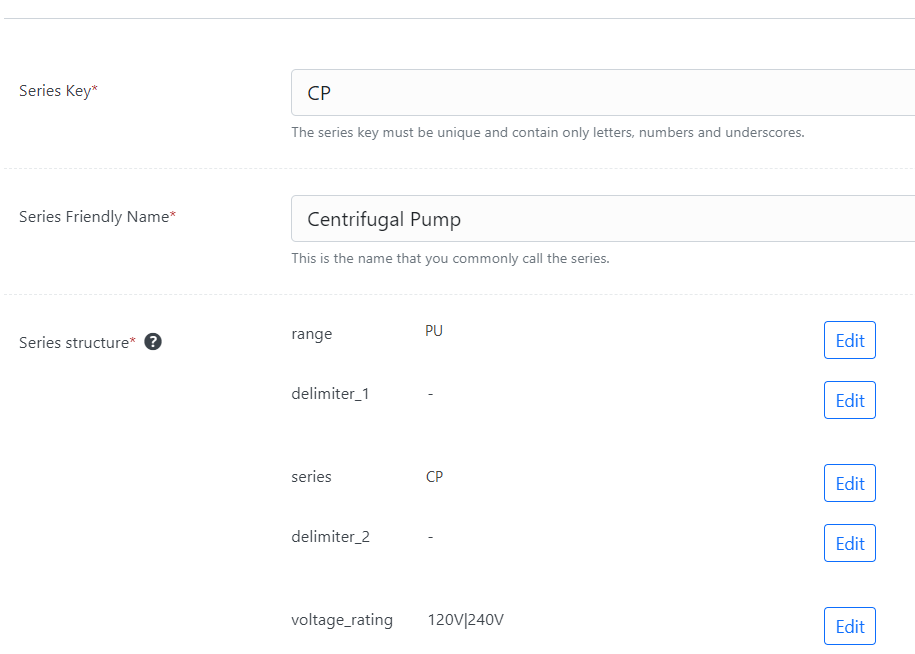
Once you have the structure defined, you can add feature data like voltage rating and control how and where features appear using simple to define rules.
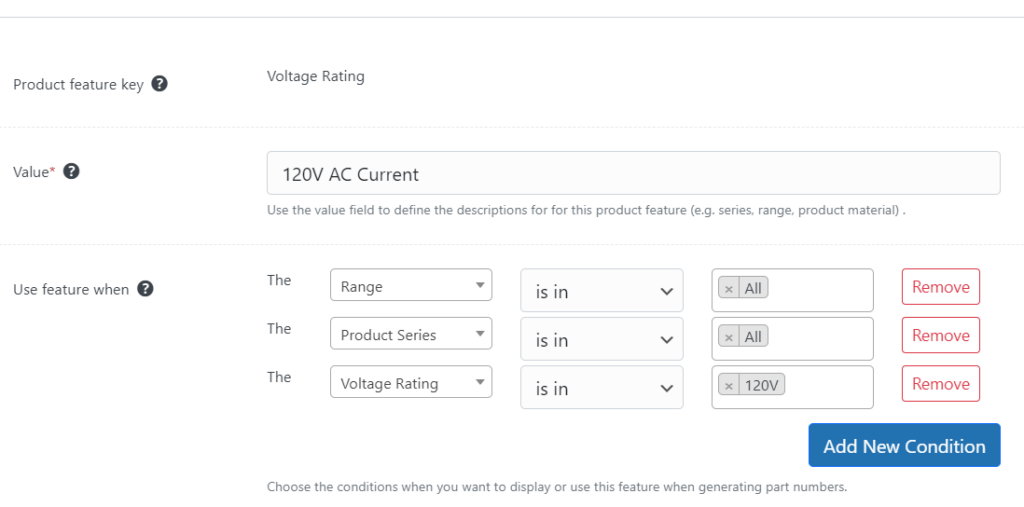
Once you have loaded your data head to the generator.
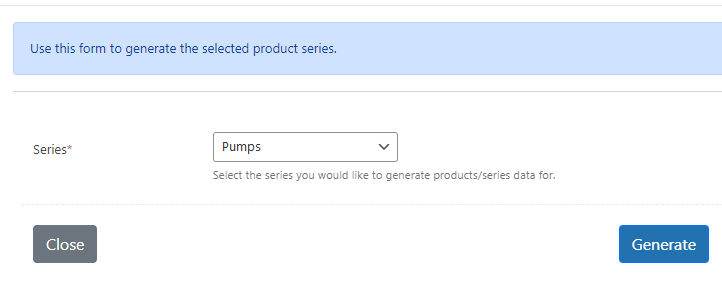
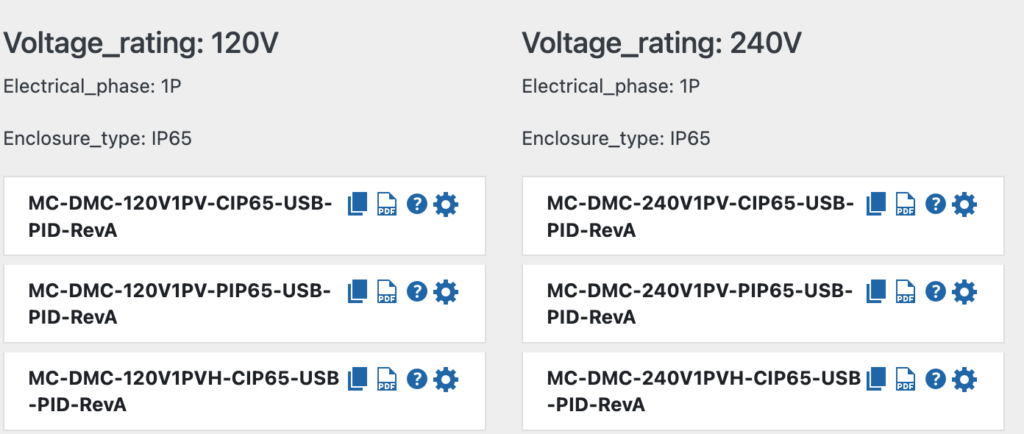
It will take seconds to generate hundreds of accurate web pages, data sheets and series overview.
(placeholder image below)
The best way to see if Product Data Engine is a good fit for your requirements is to take a look at our 3 minute product tour. We would love to show it to you and see if it is a good fit.
