Intelligent Part Numbering Scheme For Power Distribution Units
This article outlines how to create an intelligent part numbering scheme for Power Distribution Units, and how you can accurately manage this at scale
A power distribution unit (PDU) is an electrical device that is used to distribute power to multiple devices from a single power source. PDUs are commonly used in data centers, server rooms, and other environments where multiple electronic devices need to be powered and managed.
To create a part numbering scheme for PDU’s there are several characteristics you might take into consideration. Here are 9 as an example:
- Environmental rating – Indoor, Outdoor: This characteristic tells us whether the PDU is designed for indoor or outdoor use. It is important to ensure that the PDU is used in the appropriate environment and can withstand the conditions in which it will be operating.
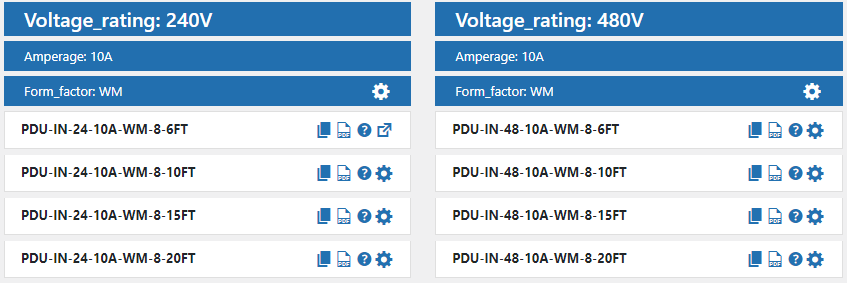
- Voltage rating – 120V, 240V, 208V: This characteristic tells us the maximum voltage that the PDU is rated for. The voltage rating is important to ensure that the PDU can safely handle the voltage level of the input power source.
- Amperage – 10A, 15A, 20A: This characteristic tells us the maximum amperage that the PDU can handle. The amperage rating is important to ensure that the PDU can safely handle the amount of current that will be drawn by the devices connected to it.
- Form factor – Tower, Rack-mount, Wall-mount: This characteristic tells us the physical design of the PDU. The form factor is important to ensure that the PDU can be mounted or installed in the appropriate location, such as a server rack or on a wall.
- Number of outlets – 8, 16, 24: This characteristic tells us the number of outlets or sockets that are available on the PDU. The number of outlets is important to ensure that there are enough connections available to power all the devices that need to be connected.
- Power cord length – 6ft, 10ft, 15ft: This characteristic tells us the length of the power cord that is attached to the PDU. The power cord length is important to ensure that the PDU can be connected to the power source at the appropriate distance.
To create the actual part number, you could assign a unique code to each option for each characteristic. For example, you could use an abbreviation for the range (e.g. PDU for Power Distribution Units) Environmental rating (e.g. “In” for Indoor, “Ou” for Outdoor), the first 2-digits of the voltage rating (e.g. “12” for 120V, “24” for 240V, etc.), and so on. Then, you can combine the codes for each characteristic to form the complete part number. For example, a PDU with the following characteristics:
- Environmental rating: Indoor
- Voltage rating: 240V
- Amperage – 15A
- Form factor – Wall-mount
- Number of outlets – 8
- Power cord length – 15ft
This might result in a part number that looks like this: “PDU-IN-24-15A-WM-8-15FT”
You can then use this part number as a unique identifier for the PDU in your inventory management system or product catalog.
How can this be done accurately at scale?
PDE is designed to make the definition, management and generation of these part number schemes easy to manage at scale.
Rules for how the product codes should work are entered into the system and then the system can generate the most complicated combinations accurately.
Setting up a the structure of a product series in PDE is straight forward.
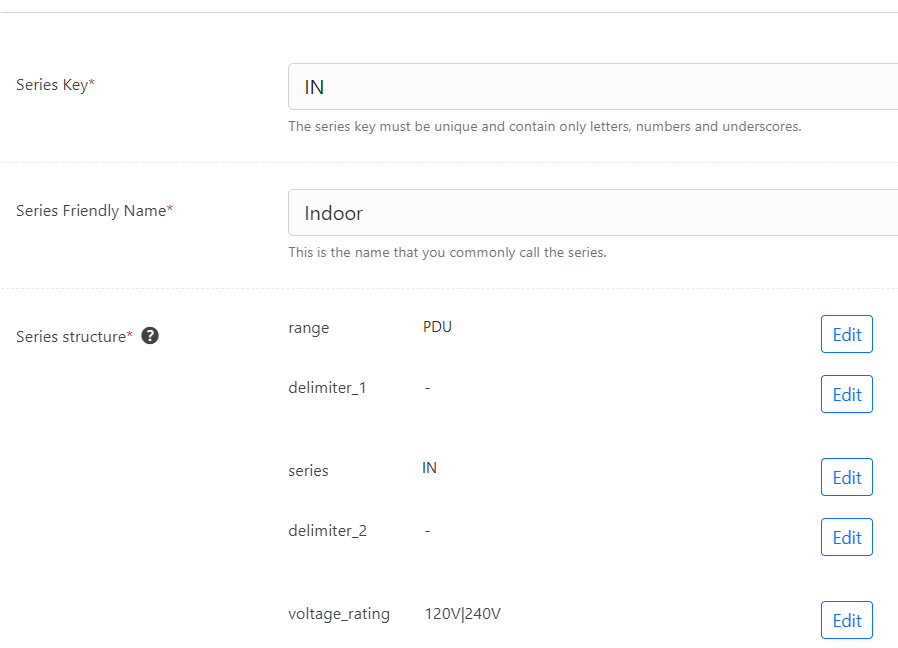
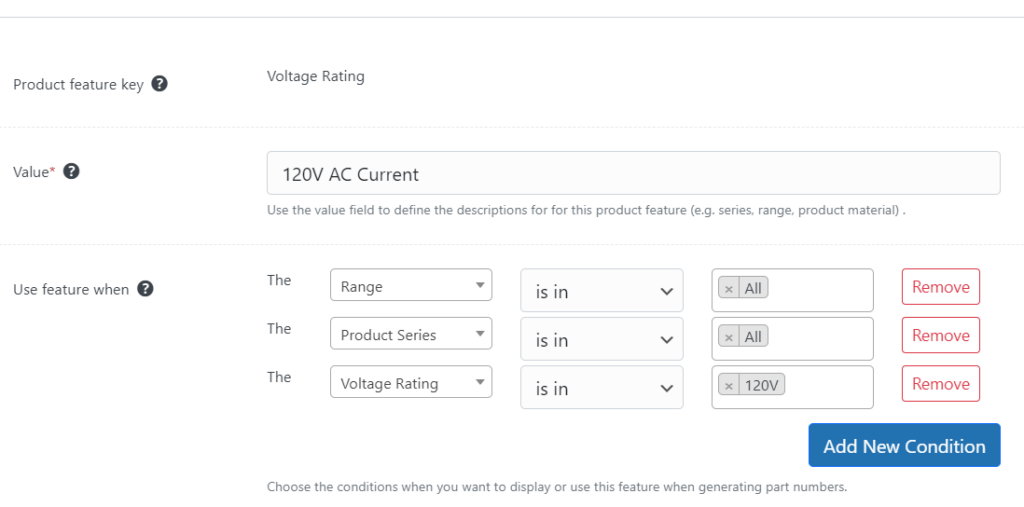
Once you have the structure defined, you can add feature data like voltage rating and control how and where features appear using simple to define rules.
Once you have loaded your data head to the generator.
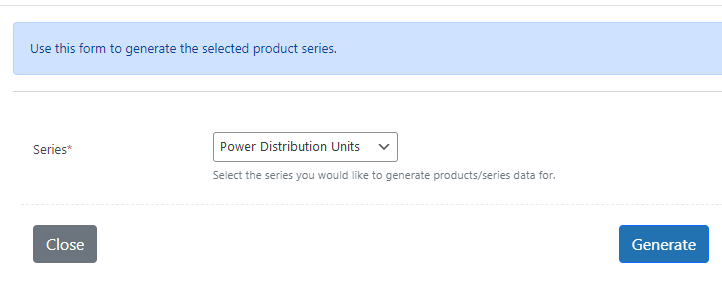
It will take seconds to generate hundreds of accurate web pages, data sheets and series overview.
The best way to see if Product Data Engine is a good fit for your requirements is to take a look at our 3 minute product tour. We would love to show it to you and see if it is a good fit.
